The Difference between True and Magnetic North
Accurate navigation is crucial when using maps for outdoor activities.
One important factor to consider is the difference between true north and magnetic north. In this article, we will explore the concept of magnetic declination and why it is essential to compensate for this difference when using a map. We will provide a step-by-step guide on how to adjust a compass and effectively compensate for the difference between true north and magnetic north.
When navigating using a map, it is important to have a reference point for direction. True north refers to the direction toward the North Pole, while magnetic north refers to the direction toward the magnetic North Pole. The difference between true north and magnetic north is known as magnetic declination. This declination value varies based on location and changes over time due to the movement of the Earth's magnetic field. To convert true north to magnetic north, you need to know the magnetic declination for your location.

Understanding True North and Magnetic North
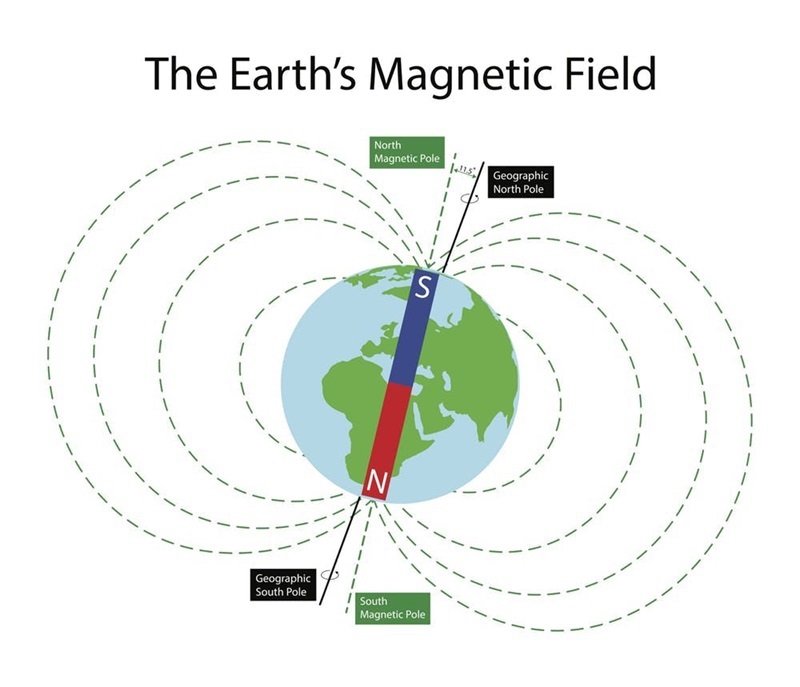
Before diving into compensating for the difference, it's essential to understand the definitions of true north and magnetic north.
True north refers to the direction towards the North Pole, the northernmost point on the Earth's axis of rotation.
Magnetic north refers to the direction towards the magnetic north pole, the point on the Earth's surface where the magnetic field lines point vertically downward.
The magnetic north pole is not fixed and is constantly moving. The magnetic north pole is located on Ellesmere Island in Northern Canada, but it is moving at a speed of about 10 kilometers per year.
The movement of the magnetic north pole has implications for navigation, as it affects the accuracy of compass readings. This phenomenon is part of the Polar Shift Theory, which suggests the possibility of a complete pole reversal. While pole reversals occur over hundreds or thousands of years and not as a quick switch, they highlight the dynamic nature of the Earth's magnetic field and its impact on navigation.
Determining Magnetic Declination
To compensate for the difference between true north and magnetic north, determine the magnetic declination for your specific location.
Maps often provide information on magnetic declination, but using reliable online resources for the most up-to-date values is advisable. These resources consider the movement of the magnetic north pole and provide accurate information for your location.
One such resource is the National Resources Canada (NRCAN) website, which offers current magnetic declination values that can be easily accessed. Staying updated with the latest magnetic declination values is crucial for accurate navigation, as these values can change over time.
In addition to online resources, there are other methods to determine magnetic declination. Some compasses have built-in declination adjustments, allowing you to set the declination value for your location.
However, it is still important to periodically check and update the adjustment due to the changing nature of magnetic declination.
Another method is to use a declination diagram, which visually represents the difference between true north and magnetic north for a specific location.
These diagrams can be found on maps or online and can be a valuable tool for determining the magnetic declination for your area.

Adjusting a Compass for Magnetic Declination
Once you have determined the magnetic declination for your location, it's time to adjust your compass.
To compensate for magnetic declination, using a compass with an adjustable declination setting is essential. This feature allows you to offset the North arrow indicators on the compass by the number of degrees of declination for your location. By adjusting the compass, you align it with the magnetic field in your area, enabling accurate navigation.
Here's more on How to Use Your Compass.
To adjust the compass for magnetic declination, follow these steps:
- Locate the declination adjustment screw or knob on your compass. This is usually found on the back or side of the compass.
- Use a small screwdriver or your fingers to adjust the declination setting. Turn the screw or knob until the compass needle aligns with the North arrow indicators on the compass.
- Set the declination value according to the magnetic declination for your location. If the magnetic declination is east, rotate the compass needle clockwise. If the magnetic declination is west, rotate the compass needle counterclockwise.
- Once the declination is set, remember to periodically check and update the adjustment to account for any changes in magnetic declination.
By adjusting your compass for magnetic declination, you ensure that the North arrow on the compass aligns with the magnetic north in your area. This alignment is crucial for accurate navigation when using a map.
Compensating for the Difference on a Map
Now that you have adjusted your compass for magnetic declination, it's time to compensate for the difference between true north and magnetic north on a map.
Various tools and resources are available to help with this process. Declination diagrams provide visual representations of the difference and can guide you in compensating for it effectively. Online tools are also available to calculate and provide accurate values for magnetic declination for your location.
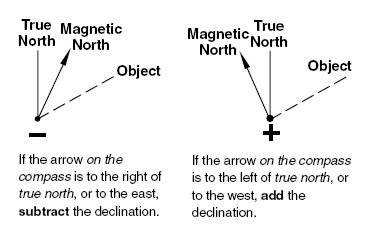
To compensate for the difference on a map, follow these steps:
- Identify the magnetic declination value for your location. This can be obtained from reliable online resources or a declination diagram.
- Locate the true north arrow on your map. This arrow represents the direction towards the North Pole.
- Subtract the magnetic declination from the true north reading on your map to obtain the magnetic north reading. This adjusted reading will guide you in the correct direction based on the magnetic field in your area.
- Use the magnetic north reading on your map to navigate accurately. By following this adjusted reading, you can account for the difference between true north and magnetic north and confidently reach your destination.
Remember, accurate compensation for the difference is crucial for successful navigation. By adjusting your compass and compensating for the difference on a map, you can confidently navigate using accurate directions.
The Movement of the Magnetic North Pole
The movement of the magnetic north pole is an important factor to consider when compensating for the difference between true north and magnetic north. As mentioned earlier, the magnetic north pole is not fixed and constantly moves at a speed of about 10 kilometers per year. This movement has implications for navigation, as it affects the accuracy of compass readings.
The phenomenon of the movement of the magnetic north pole is part of the Polar Shift Theory, which suggests the possibility of a complete pole reversal. While pole reversals occur over hundreds or thousands of years and not as a quick switch, they highlight the dynamic nature of the Earth's magnetic field and its impact on navigation. It is important to stay updated with the latest magnetic declination values to ensure accurate navigation. As the magnetic north pole continues to move, the magnetic declination values for different locations may change over time.
Understanding the movement of the magnetic north pole and its impact on navigation helps us appreciate the complexity of Earth's magnetic field. It is a constant reminder that our planet is constantly changing, and as outdoor enthusiasts, we must adapt and adjust our navigation techniques accordingly.
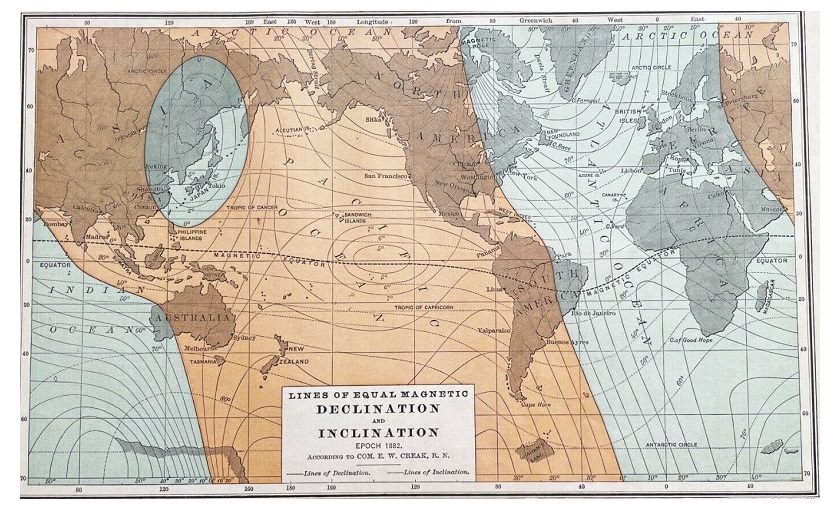
Historical Significance of Declination
The concept of declination has played a significant role in navigation throughout history. Early sailors and explorers relied on accurate navigation to traverse the oceans and discover new lands. In 1700, Edmund Halley produced the world's first declination chart, which provided valuable information for sailors and explorers. This chart helped them understand the difference between true north and magnetic north and navigate more accurately.
Declination has been critical in early exploration and cartography, enabling accurate mapping and navigation. It allowed explorers to plot their routes, mark their positions, and accurately estimate distances traveled. Early navigators would have faced significant challenges in their journeys without a proper understanding of declination.
Understanding the historical significance of declination helps us appreciate its importance in developing navigation techniques and tools. It serves as a reminder of the advancements made in navigation over the centuries and the efforts of early explorers to conquer new territories.
Conclusion
Compensating the difference between true and magnetic north on a map is crucial for accurate navigation. By understanding the concepts of true north, magnetic north, and magnetic declination, you can effectively adjust your compass and compensate for the difference.
Remember to determine the magnetic declination for your location using reliable resources and periodically update your compass's adjustment. By accurately compensating for the difference, you can navigate with confidence and precision. The movement of the magnetic north pole and the historical significance of declination further highlight the importance of understanding and compensating for this difference when using a map for outdoor activities.
/1004/site-assets/logo.png)
/1004/site-assets/phone.png)
/1004/site-assets/cart.png)
/1004/site-assets/dateseal.jpg)
/1004/site-assets/creditcards.png)